

They usually indicate permanent tissue injury.Ĭhronic compartment syndrome causes pain or cramping during exercise. Numbness or paralysis are late signs of compartment syndrome.There may also be tingling or burning sensations (paresthesias) in the skin.Using or stretching the involved muscles increases the pain. The pain is more intense than what would be expected from the injury itself.The classic sign of acute compartment syndrome is pain, especially when the muscle within the compartment is stretched. This is usually relieved by discontinuing the exercise, and is usually not dangerous. Athletes who participate in activities with repetitive motions, such as running, biking, or swimming, are more likely to develop chronic compartment syndrome. The pain and swelling of chronic compartment syndrome is caused by exercise. If you have a cast, contact your doctor immediately.Ĭhronic (Exertional) Compartment Syndrome If symptoms of compartment syndrome develop, remove or loosen any constricting bandages. Casts and tight bandages may lead to compartment syndrome. Taking steroids is a possible factor in compartment syndrome. This can happen after severe intoxication with alcohol or other drugs. The development of compartment syndrome in this manner usually occurs in people who are neurologically compromised. Most healthy people will naturally move when blood flow to a limb is blocked during sleep. Lying for too long in a position that blocks a blood vessel, then moving or waking up can cause this condition. A blood vessel can also be blocked during sleep. This may occur after a surgeon repairs a damaged blood vessel that has been blocked for several hours. Reestablished blood flow after blocked circulation.This type of injury can occur when a motorcycle falls on the leg of the rider, or a football player is hit in the leg with another player's helmet. Conditions that may bring on acute compartment syndrome include:.Rarely, it develops after a relatively minor injury. It can also occur in other compartments in the leg, as well as in the arms, hands, feet, and buttocks.Īcute compartment syndrome usually develops after a severe injury, such as a car accident or a broken bone. This does not usually happen in chronic (exertional) compartment syndrome.Ĭompartment syndrome most often occurs in the anterior (front) compartment of the lower leg (calf). In acute compartment syndrome, unless the pressure is relieved quickly, permanent disability and tissue death may result. Without a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients, nerve and muscle cells can be damaged. Blood flow to muscle and nerve cells is disrupted. Because the fascia does not stretch, this can cause increased pressure on the capillaries, nerves, and muscles in the compartment. © American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2003.Ĭompartment syndrome develops when swelling or bleeding occurs within a compartment. Figure B: Reproduced and adapted from The Body Almanac.
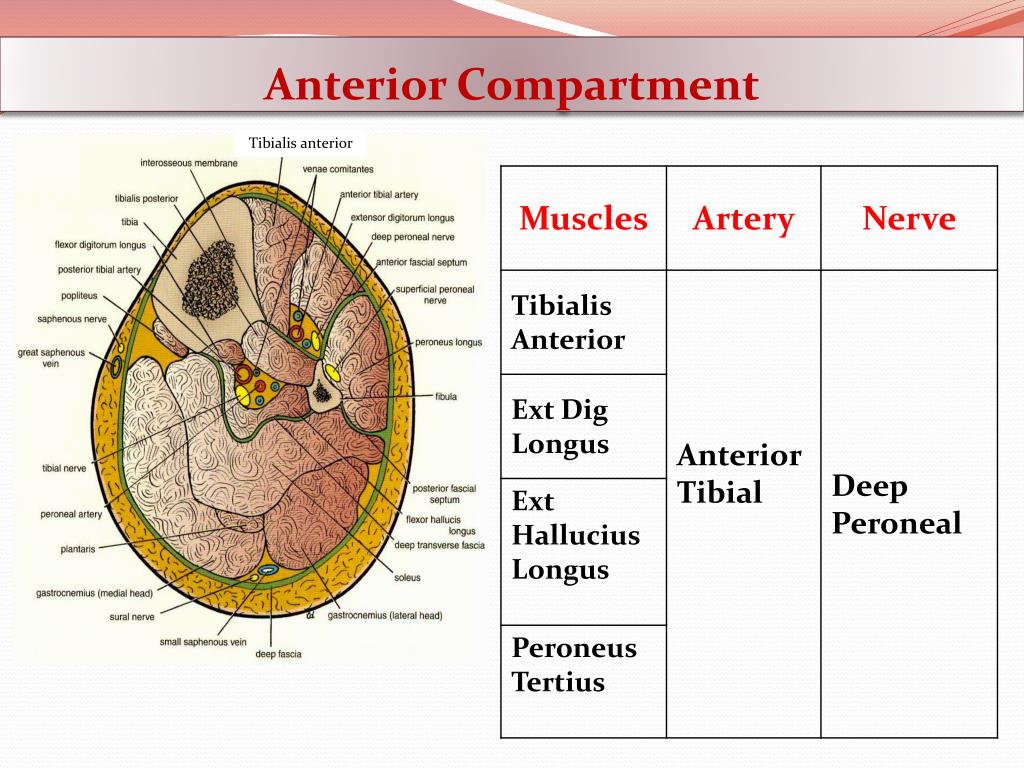
Rosemont, IL, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2000. The area between the knee and ankle has four major muscle compartments: anterior, lateral, superficial posterior, deep posterior.įigure A: Reproduced and adapted with permission from Gruel CR: Lower Leg, in Sullivan JA, Anderson SJ (eds): Care of the Young Athlete. The role of the fascia is to keep the tissues in place, and, therefore, the fascia does not stretch or expand easily. Covering these tissues is a tough membrane called a fascia. It is most often caused by athletic exertion.Ĭompartments are groupings of muscles, nerves, and blood vessels in your arms and legs. Without treatment, it can lead to permanent muscle damage.Ĭhronic compartment syndrome, also known as exertional compartment syndrome, is usually not a medical emergency. This pressure can decrease blood flow, which prevents nourishment and oxygen from reaching nerve and muscle cells.Ĭompartment syndrome can be either acute or chronic.Īcute compartment syndrome is a medical emergency. Compartment syndrome is a painful condition that occurs when pressure within the muscles builds to dangerous levels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
