
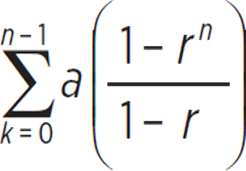
Sum of geometric sequence proof series#
If the terms get larger as the series progresses, the series diverges.

The common ratio must be between -1 and 1.Ī geometric series diverges and does not have a sum to infinity if |r|≥1. Geometric series converge and have a sum to infinity if |r|<1. The series converges because the terms are getting smaller in magnitude. Therefore the fractions will fill an area of. The series converges to a final value.įor example, in the series, the fractions can be seen to fit inside the area of a 1 by 1 square. This means that the terms being added to the total sum get increasingly small. If |r|<1, the sequence will converge to the sum to infinity given by S ∞=a/(1-r).Ī convergent geometric series is one in which the terms get smaller and smaller. If the common ratio is outside of this range, then the series will diverge and the sum to infinity will not exist. The sum to infinity only exists if -1
Sum of geometric sequence proof how to#
How to Find the Sum to Infinity of a Geometric Series This means that the sequence sum will approach a value of 8 but never quite get there. The sum of an infinite number of terms of this series is 8. The sum to infinity of the series is calculated by, where is the first term and r is the ratio between each term.įor this series, where and, which becomes. We can see that the sum is approaching 8.Įventually, if an infinite number of terms could be added, the sum would indeed approach 8. īecause the terms are getting smaller and smaller, as we add more terms, we are adding an increasingly negligible amount. As more terms are added, we see that, , and.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
